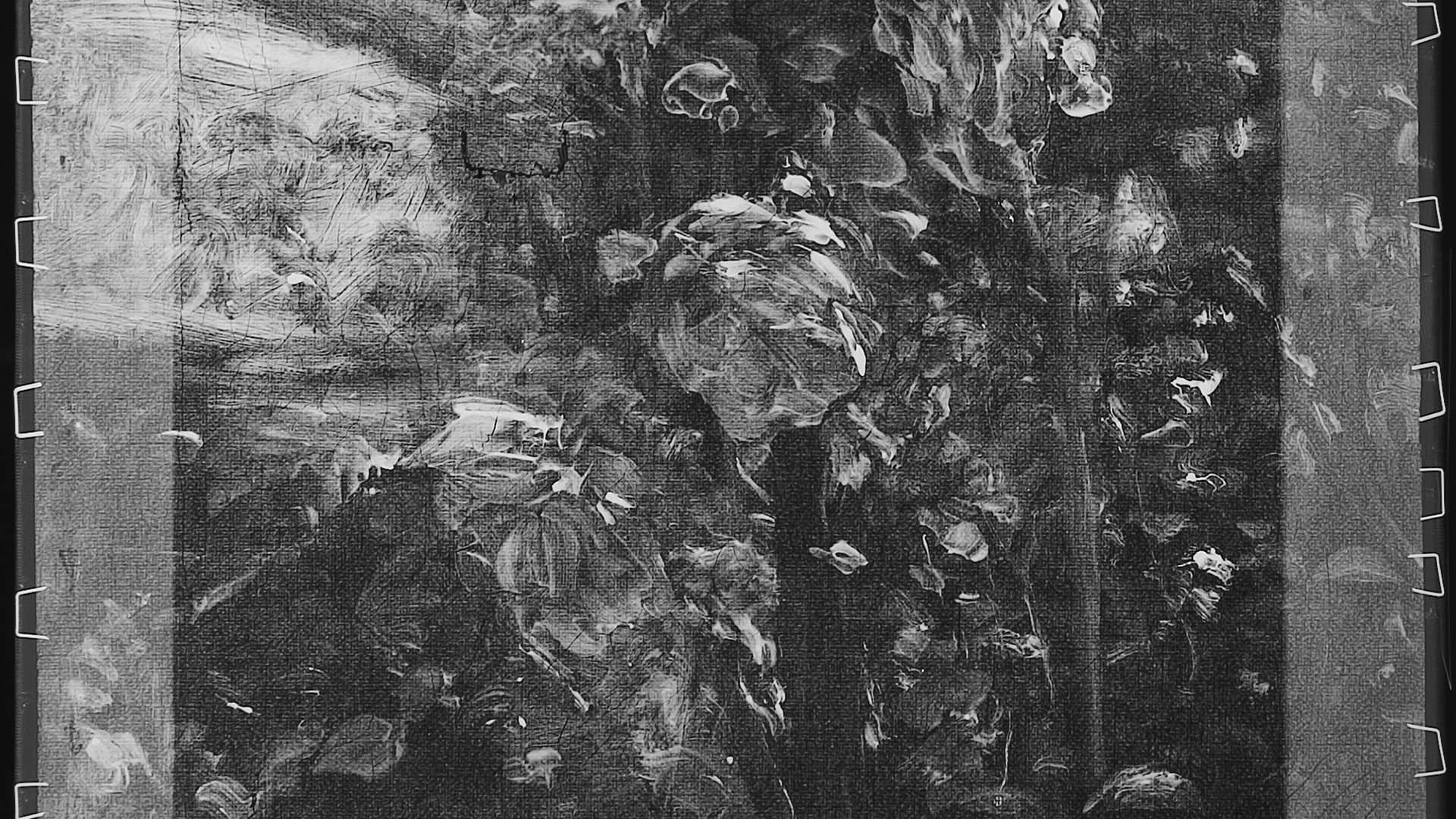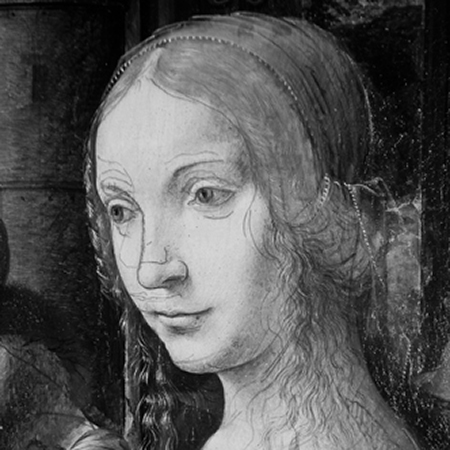IMAGING ANALYSIS
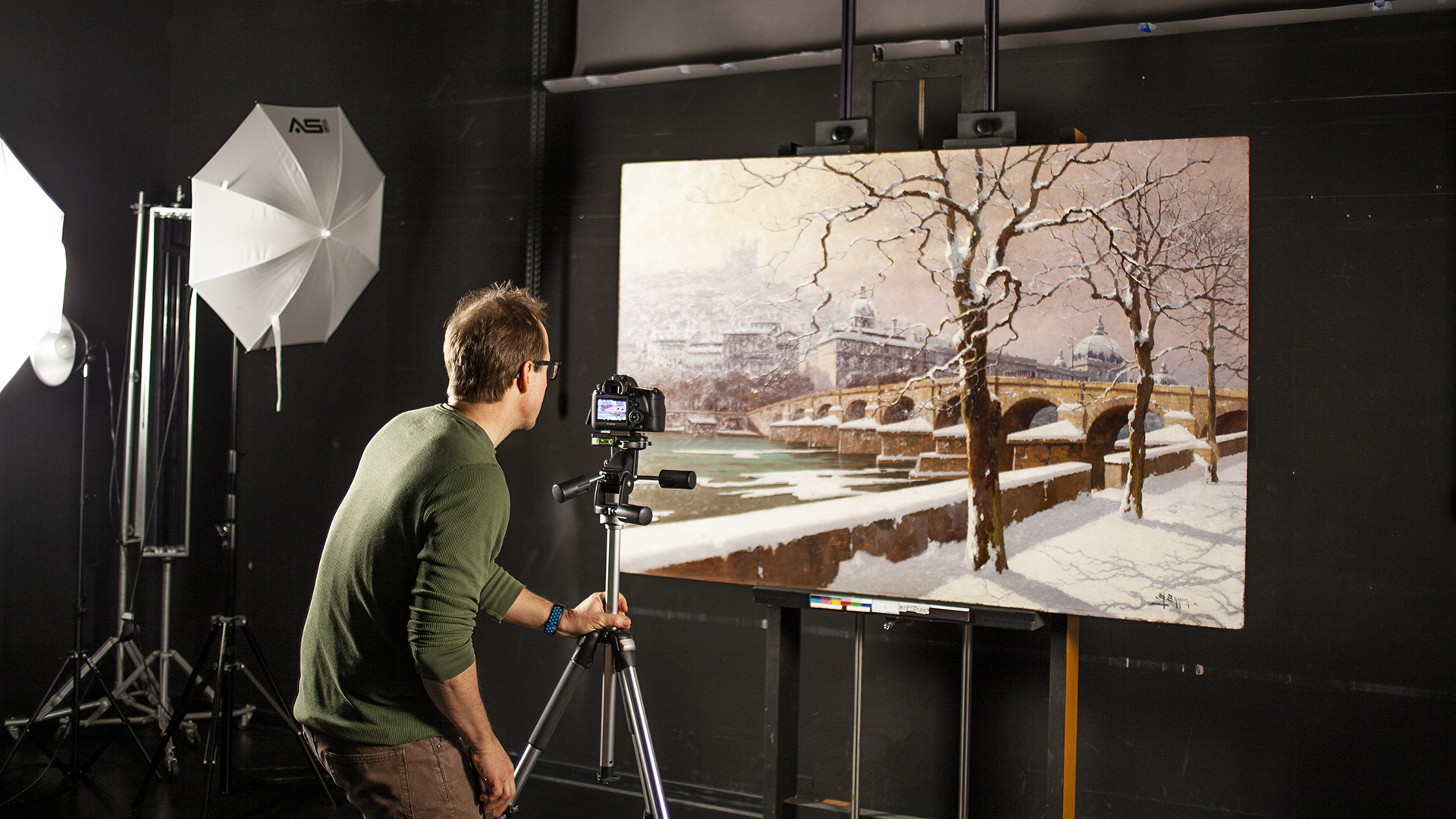
The Center offers imaging services to meet two distinct needs: to examine artworks in preparation for conservation, and to document items before and after treatment.
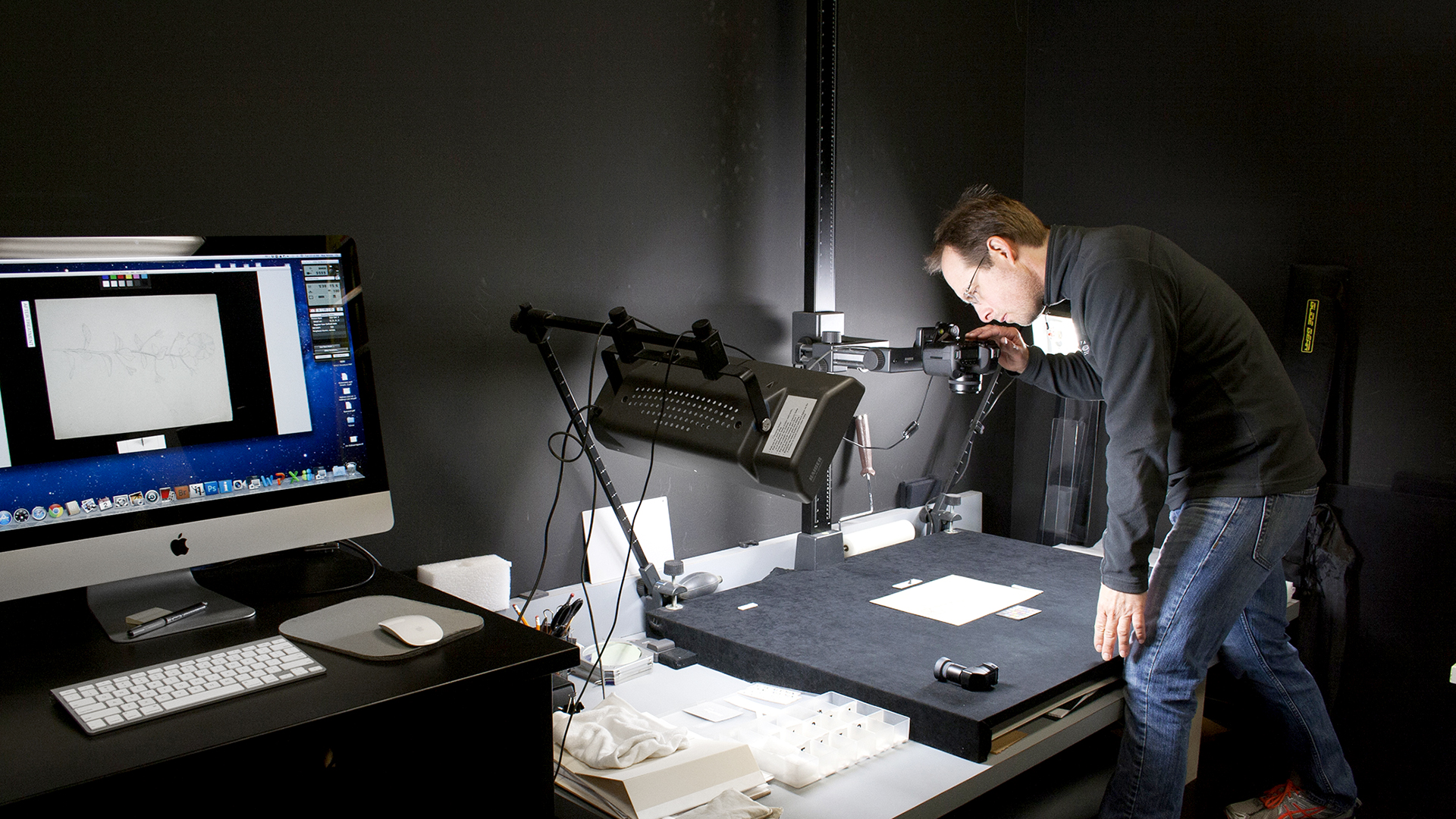
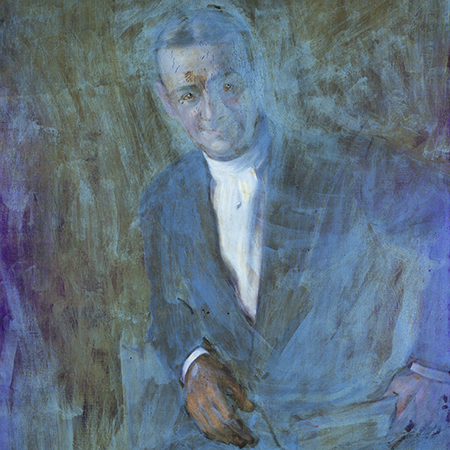
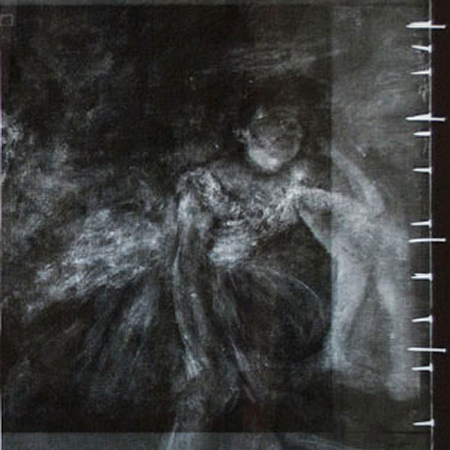
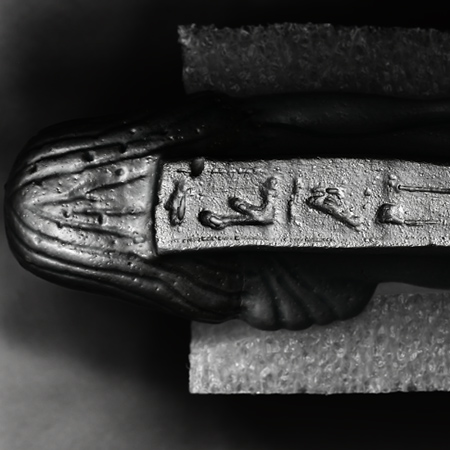
Before beginning work, conservators may employ a number of imaging techniques to explore the layers of an artwork that are visible and invisible to the naked eye. Some of these approaches employ standard digital photography and specialized lighting, while others involve equipment capable of producing or capturing electromagnetic wavelengths above or below the narrow band of the visible spectrum. WACC provides all approaches, including:
- Diagnostic photography in raking and reflective light
- Long-wave ultraviolet photography
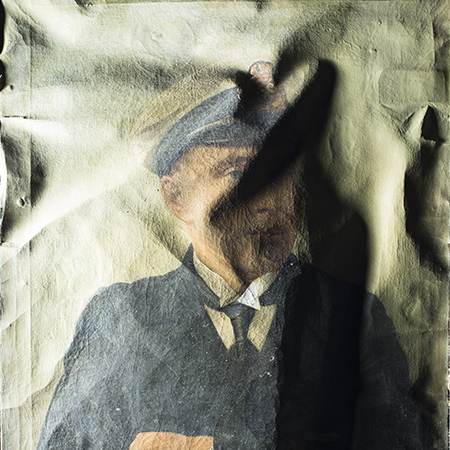
- Infrared photography
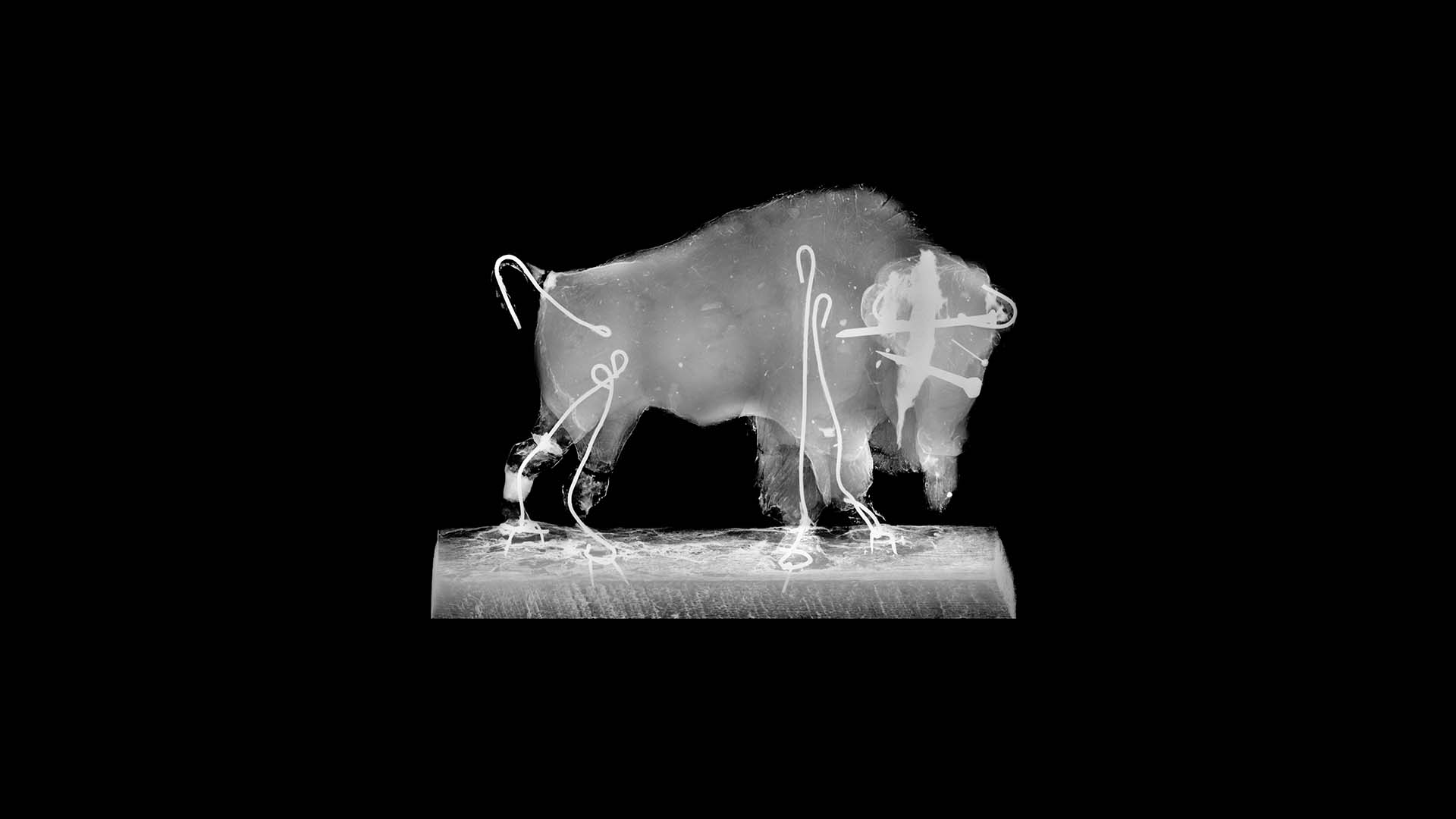
- Radiography
- Reflectance Transmittance Imaging (RTI)
Diagnostic photography provides useful evidence of the surface condition of artworks.
Everything conserved by WACC is photographed to provide a visual document of treatment history. Documentary imaging records all stages of the conservation process, including the object’s condition before treatment, during treatment at key stages of the work, and after treatment is complete. This documentation is useful to the client in understanding all aspects of the treatment, and creates a record of procedure and condition for future curatorial and conservation reference.
s