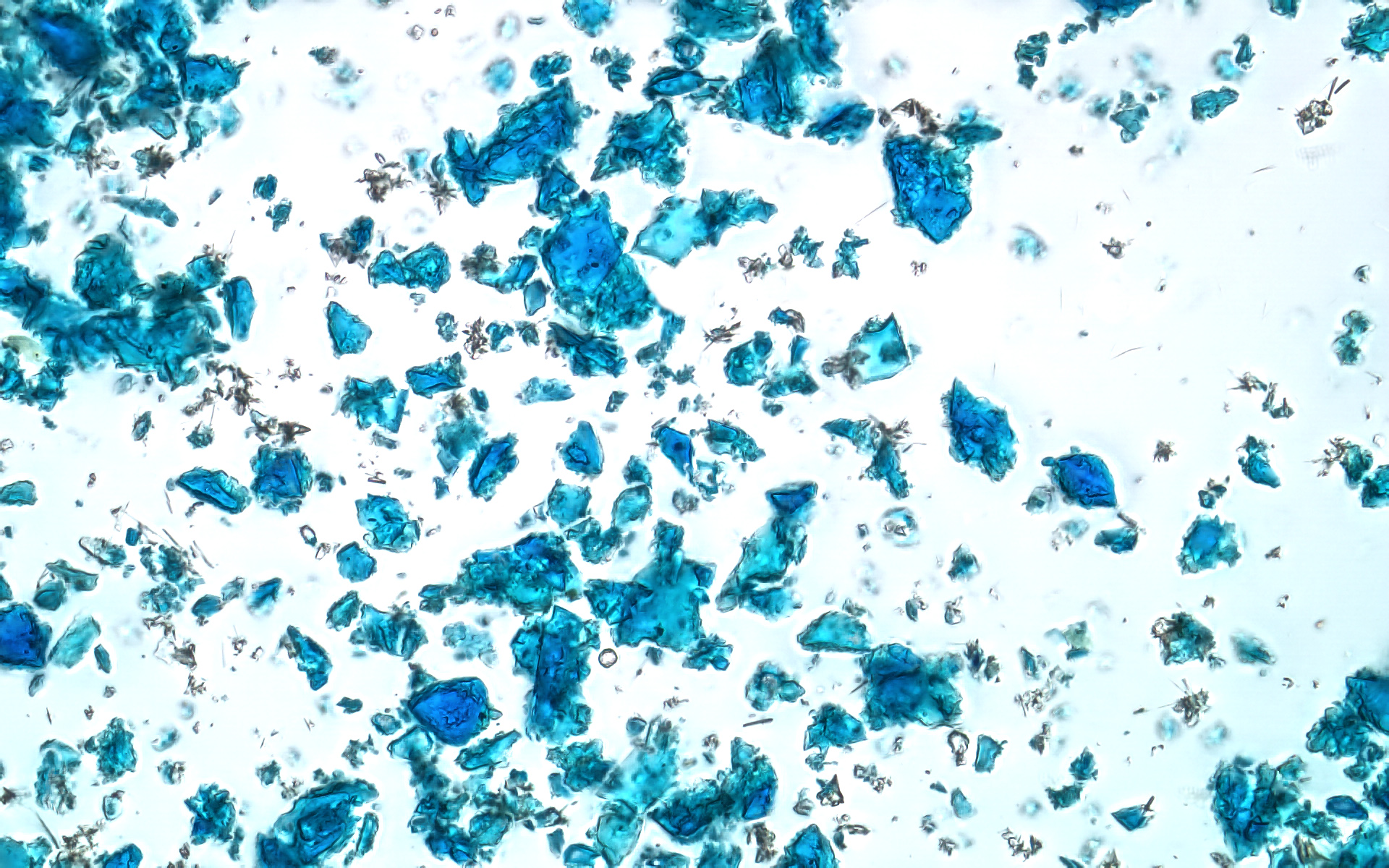
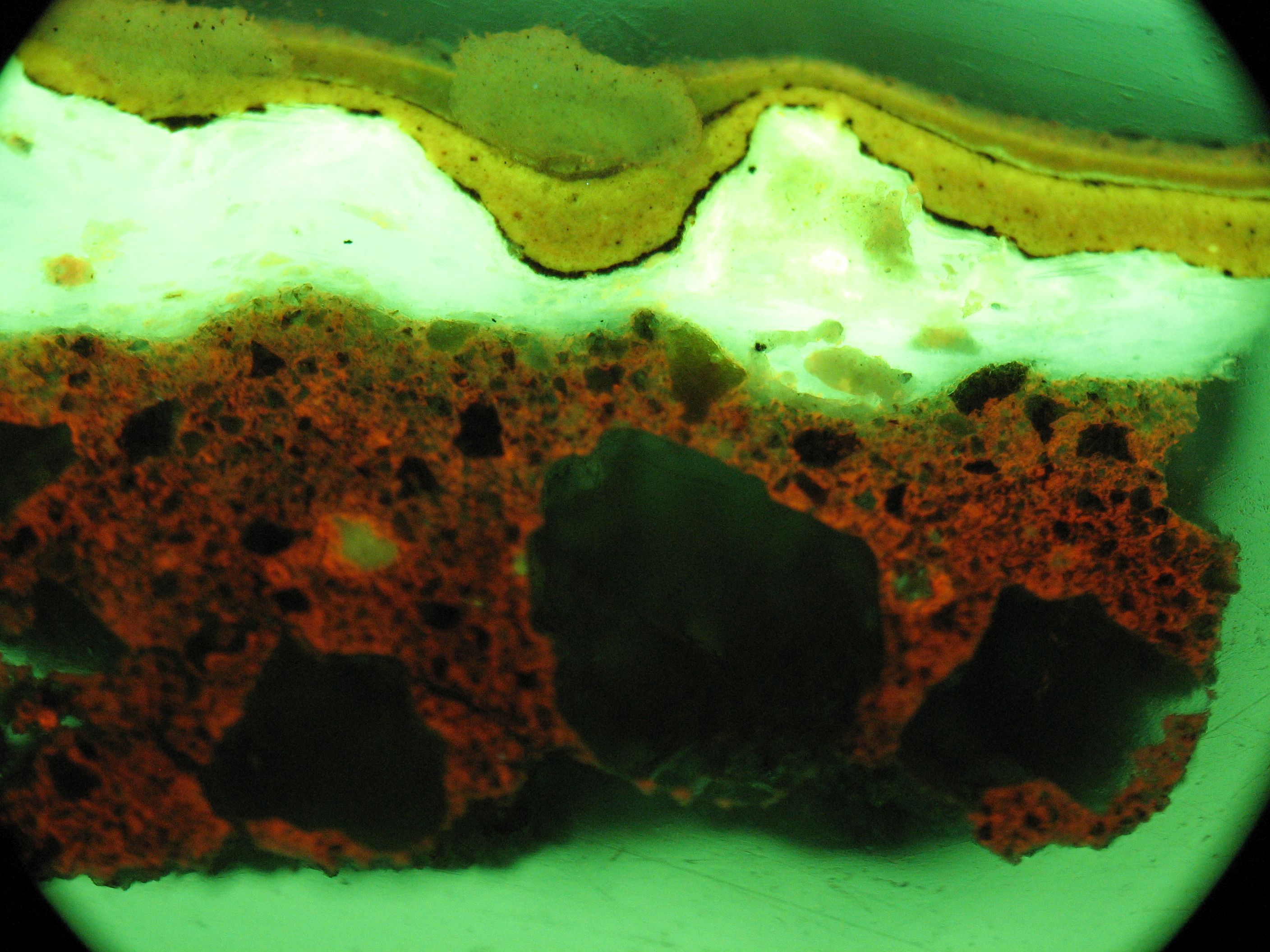
SCIENTIFIC ANALYSIS OF ART MATERIALS FOR CONSERVATION
The Department of Scientific Analysis was established to serve members, non-profit institutions and laboratories, corporate clients, and private collectors. We use material analysis to inform treatment and conduct technical analysis on artworks for our clients.
Material analysis provides an understanding of the material(s) from which an object is made. It is also used to characterize changes that have occurred due to deterioration and previous interventions. This type of information aids the conservator in determining the best plan for preservation and treatment. Conservation techniques may be improved by systematic comparative experiments which also require scientific analysis.
Space
For art historians, museum curators, and archaeologists, the physical composition of an object often has historical and cultural meanings revealed by material analysis. Material characterization for the purpose of technical analysis is used to provide evidence about the origin, age, and composition of an object. It is used to understand the meaning and making behind art. Examples of the types of analysis include the identification of pigments and binding media in paintings or elements in metals and glass.
Space
Inorganic and organic analysis is often coupled with various imaging techniques, such as x-radiography and infrared reflectography, to understand the meaning and making of art works.
Space
Range of analytical techniques available:
Space
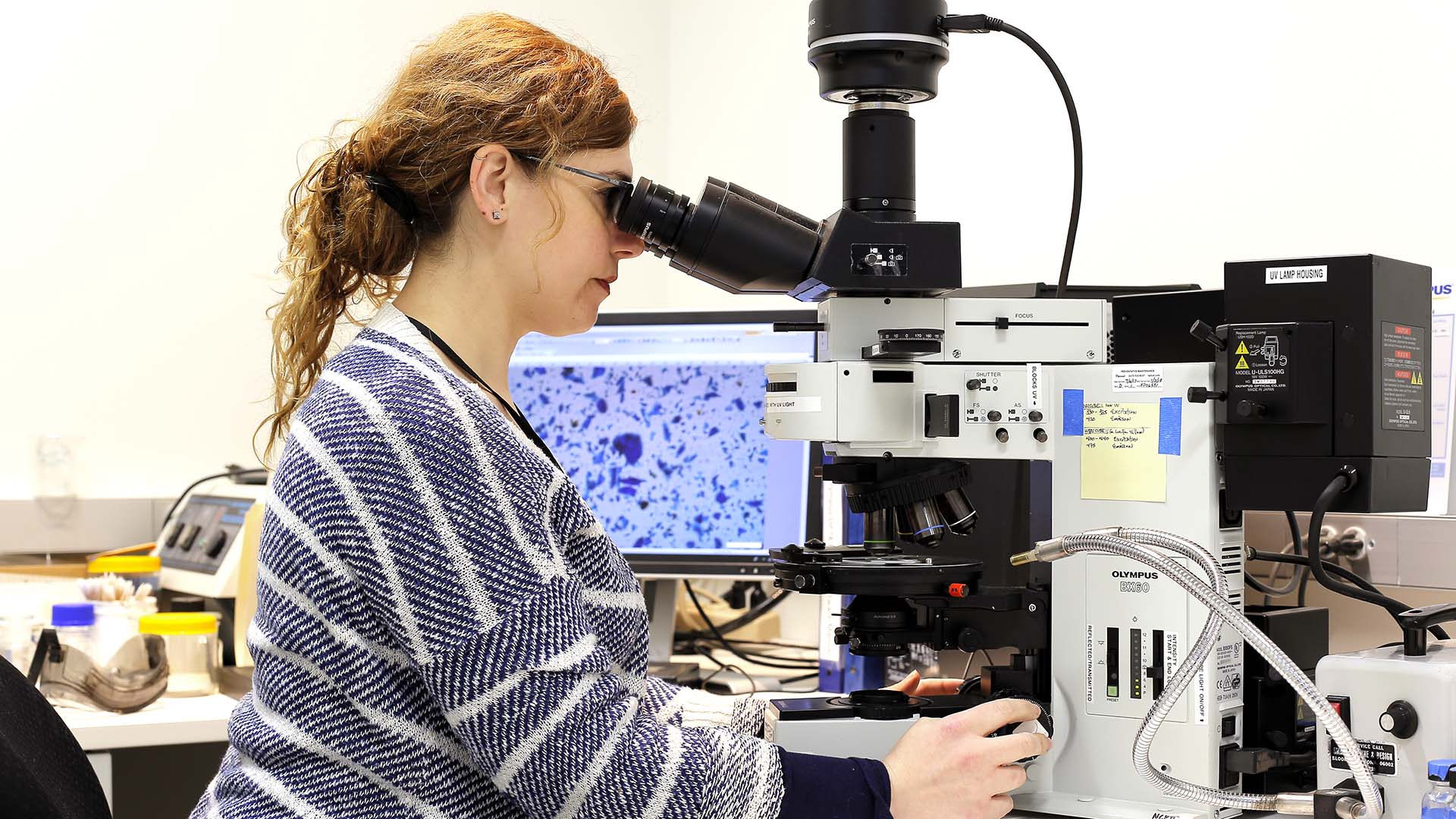
- Optical Microscopy
- Micro-FTIR Spectrometry
- SEM-EDS
- GC-MS
- XRF (portable)
- XRD
- UV-VIS Spectrometry
- LC-DAD-MS
- LC-Ion trap MS
- Laser Raman Spectrometry
- MALDI-TOF-MS